What is Git Stash:
Git stash is a command that allows you to temporarily save changes you have made in your working directory, without committing them. This is useful when you need to switch to a different branch to work on something else, but you don't want to commit the changes you've made in your current branch yet.
To use Git Stash, you first create a new branch and make some changes to it. Then you can use the command git stash to save those changes. This will remove the changes from your working directory and record them in a new stash. You can apply these changes later. git stash list command shows the list of stashed changes.
You can also use git stash drop to delete a stash and git stash clear to delete all the stashes.
What is Cherry-pick?
Git cherry-pick is a command that allows you to select specific commits from one branch and apply them to another.
This can be useful when you want to selectively apply changes that were made in one branch to another.
To use git cherry-pick, you first create two new branches and make some commits to them.
git cherry-pick <commit_hash>
#command to select the specific commits from one branch
#and apply them to the other.
What are Resolving Conflicts?
Conflicts can occur when you merge or rebase branches that have diverged, and you need to manually resolve the conflicts before it can proceed with the merge/rebase.
git status
#command shows the files that have conflicts
git diff
#command shows the difference between the conflicting versions
git add
#command is used to add the resolved files.
Task 1:
Create a new branch and make some changes to it.
git init git checkout -b stash-b touch testfile.txt vim testfile.txt git add .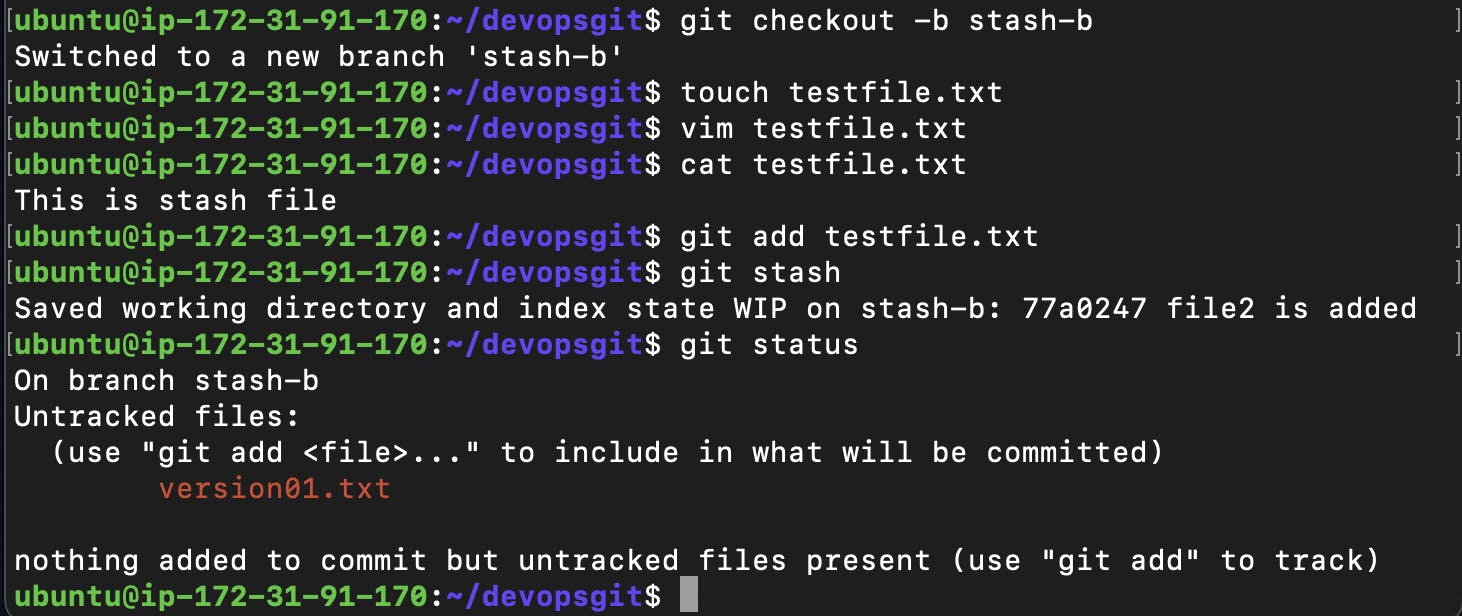
Use git stash to save the changes without committing them.
git stash git statusSwitch to a different branch, make some changes and commit them.
git checkout dev
Use git stash pop to bring the changes back and apply them on top of the new commits.

Task 2:
In version01.txt of development branch add below lines after “This is the bug fix in development branch” that you added in Day10 and reverted to this commit.
git init git touch version01.txt vim version01.txt cat version01.txt This is the bug fix in development branchLine2>> After bug fixing, this is the new feature with minor alterations”
Commit this with the message “ Added feature2.1 in development branch”
vim version01.txt : “ Added feature2.1 in development branch” git add . git commitLine3>> This is the advancement of previous feature
Commit this with message “ Added feature2.2 in development branch”
vim version01.txt : “Added feature2.2 in development branch” git add . git commitLine4>> Feature 2 is completed and ready for release
Commit this with message “ Feature2 completed”
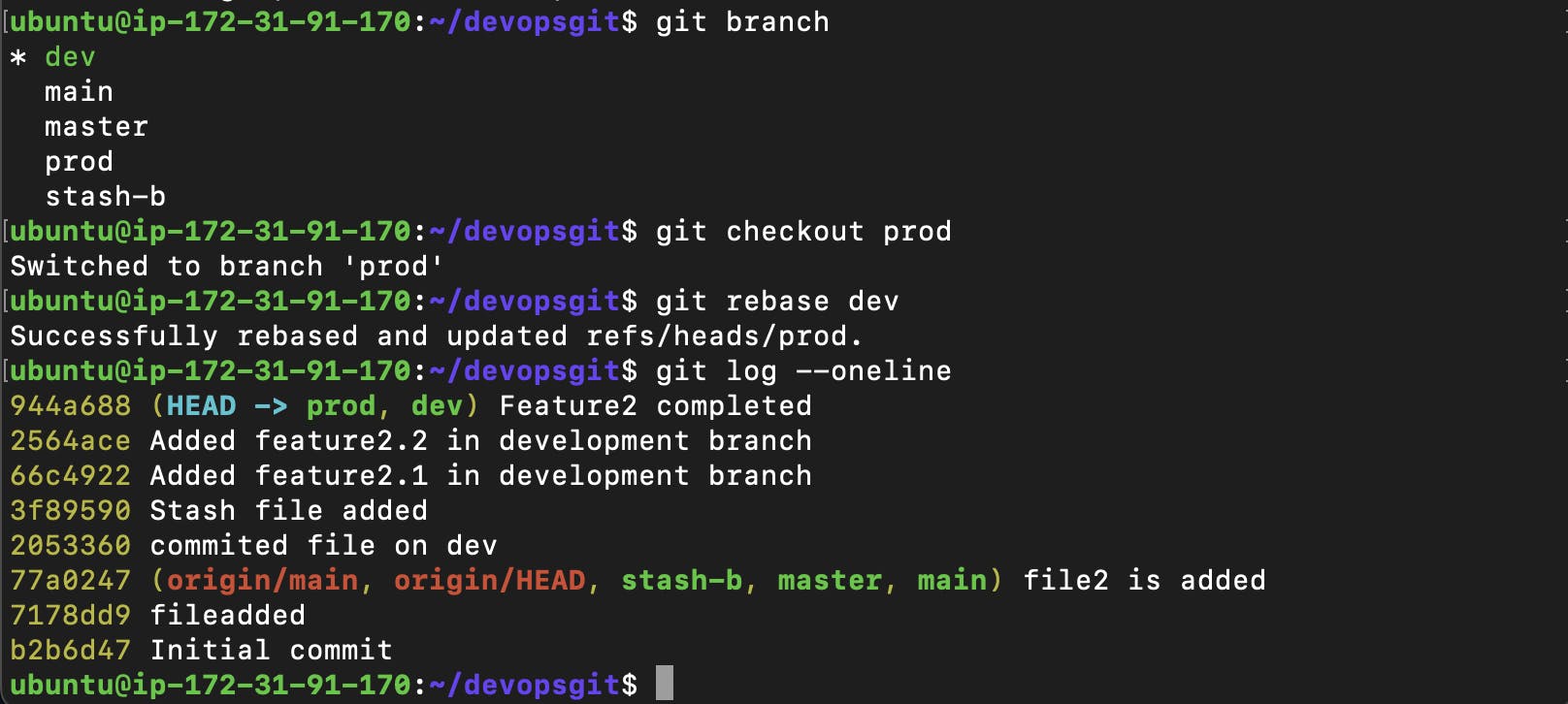
vim version01.txt : “Feature2 completed” git add . git commitAll these commits messages should be reflected in Production branch too which will come out from Master branch (Hint: try rebase).
git branch git checkout prod git rebase dev git log --oneline